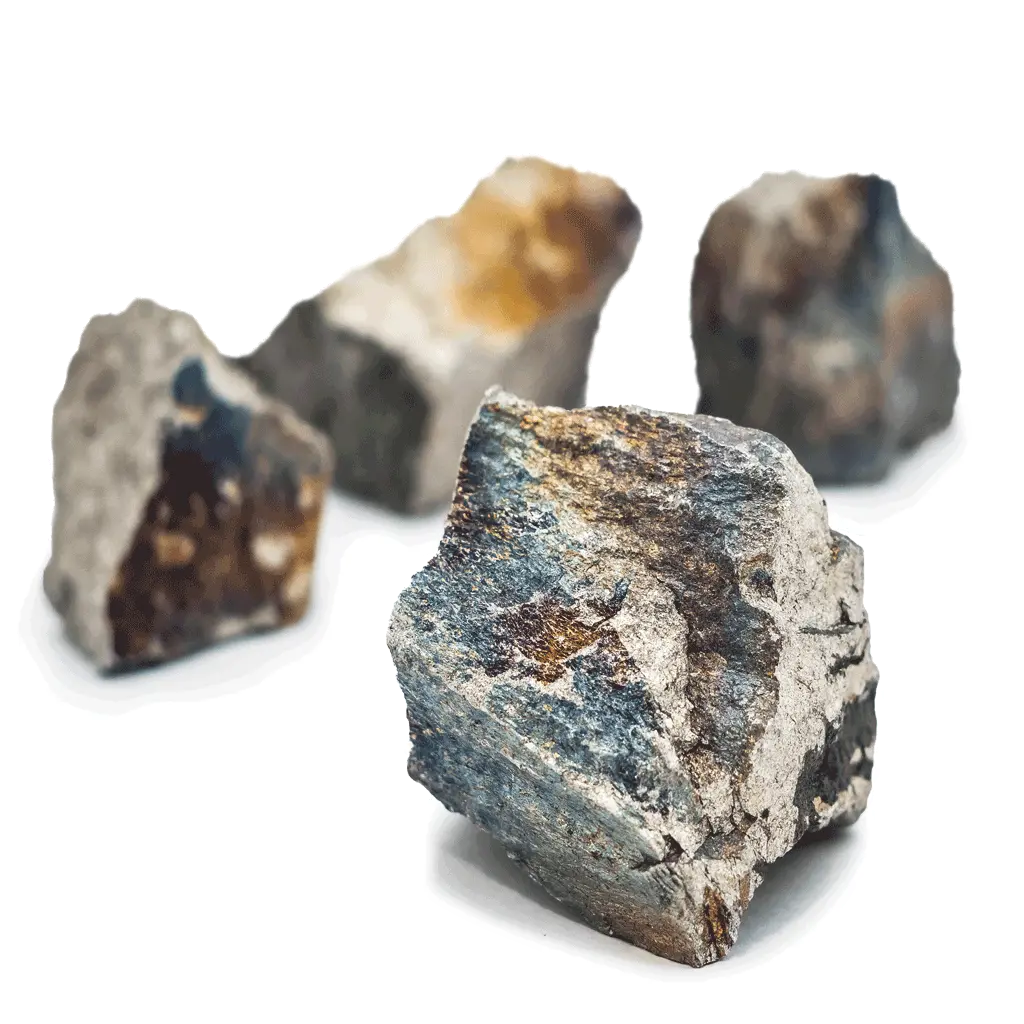
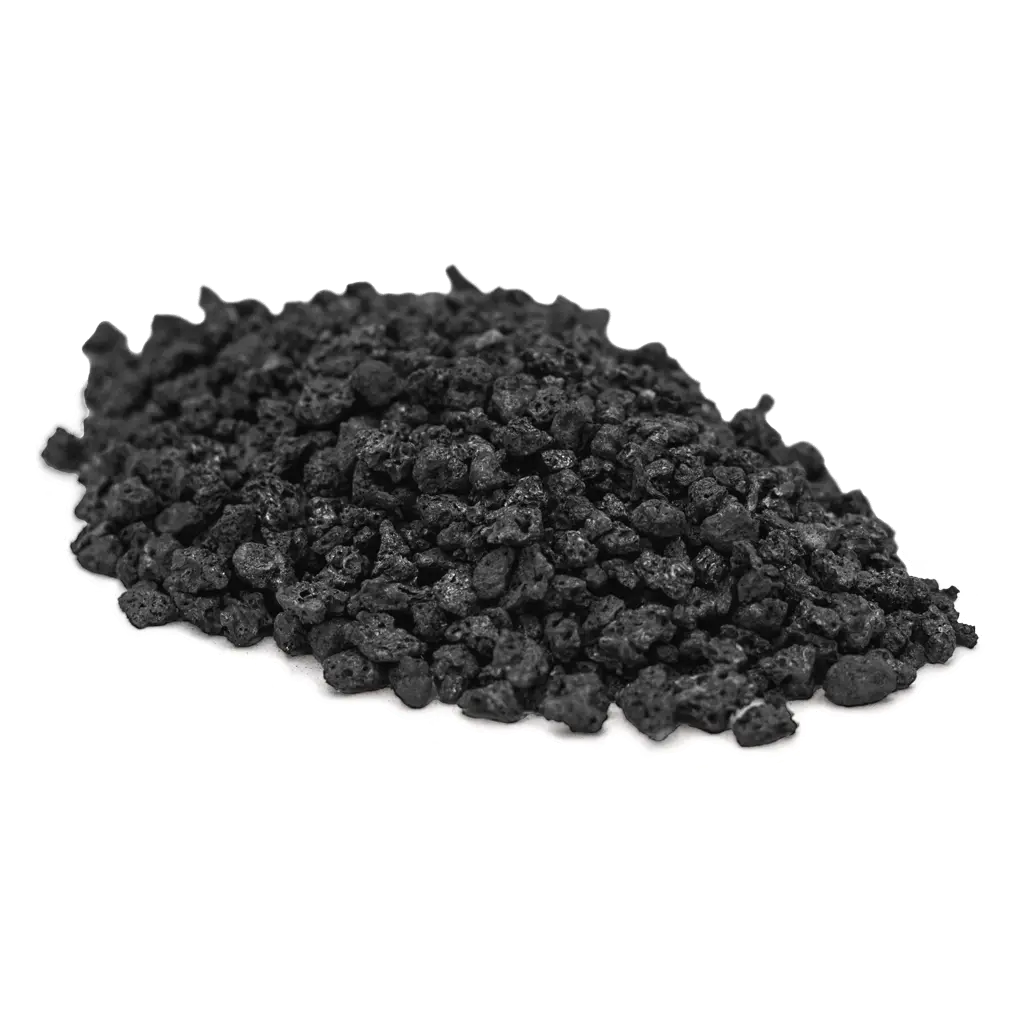
Limestone
Limestone is a type of sedimentary rock that is mainly composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), usually in the form of calcite or aragonite. It is formed when calcium carbonate minerals precipitate out of water that contains dissolved calcium. This can happen through both biological and nonbiological processes.
Applications of limestone:
Limestone has many benefits for various fields and applications. Some of the benefits of limestone are:
- It is a source of lime, which is used for making cement, concrete, glass, and agriculture. Lime is also used for neutralizing acidic soils and water.
- It is a building stone that is widely used for flooring, exterior and interior facings, and monuments. It has a natural beauty and durability that can enhance the appearance of any structure.
- It is a decorative floor covering that comes in different colors and textures. Travertine tile is a form of banded limestone that is popular for its aesthetic appeal
- It is a soil conditioner that can improve the fertility and drainage of the soil. It can also increase the availability of nutrients for plants and animals in ponds.
- It is an insulator that can help keep the temperature of your home constant. It can reduce the cost of heating and cooling your house.
- It is a reservoir rock that contains about 30% of the world’s petroleum resources. It can provide valuable information on the geologic history and evolution of life on Earth.
Processing of limestone:
Processing of limestone is a process that involves several steps, which are:
- Quarrying: Limestone is extracted from the earth’s crust through the process of quarrying. This involves drilling and blasting the rock to break it into smaller pieces.
- Crushing and screening: The extracted limestone is then crushed and screened to different sizes according to the needs of the customer or the end product. This can be done using a crusher or a hammer mill.
- Grinding: The crushed limestone is then ground into a fine powder in a grinding mill. This increases the surface area and the reactivity of the limestone.
- Calcination: The limestone powder is then heated in a kiln to produce calcium oxide (also known as quicklime). This is a chemical reaction that removes carbon dioxide from the limestone and releases heat.
- Hydration: The quicklime can then be reacted with water to form hydrated lime (also known as slaked lime). This is